What is Energy?
Simply defined, energy is the power derived from the utilization of various physical and chemical resources, which is used for lighting, heating and to operate machines.
The electricity that is used in most homes is the electrical power that was probably generated by burning coal, petroleum and natural gas or through nuclear fission or the more conventional hydroelectric plant that taps the force from a river flowing downstream to generate electricity. The common factor with these sources of energy other than hydroelectric is that they are non-renewable, hence not very environment friendly.
However, energy is the most required resource, and probably the most polluting as well. Over 40% of the global energy consumption is directly attributable to the buildings we live and work out of. Normally, requirements are met by conventional sources such as hydro, thermal or nuclear energy. There is environmental hazard in all these, though in the case of hydro it may be less when compared to thermal energy and nuclear energy.
Although there is general awareness about sustainable energy and sustainable buildings that use green energy, the awareness has not spread far and fast enough as is evident from the following image that clearly shows that only 10% of energy generated worldwide is renewable:
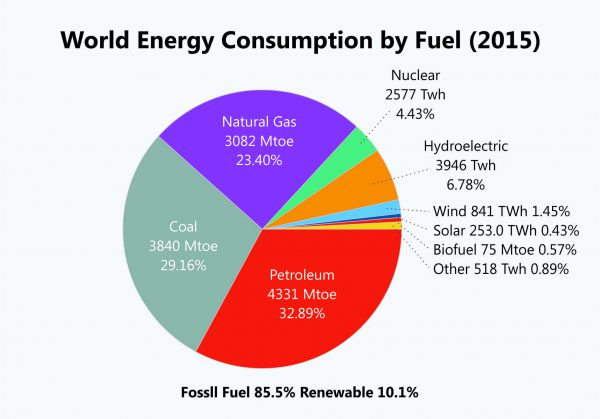
It is the fervent wish of every environmental activist to make this 10% figure at least 75% in the next few years, which is the only way to save the planet from the catastrophe it is facing due to perpetual pollution caused by the use of fossil fuels. Interestingly, although solar energy is available in unmeasurable quantities, it accounts for less than 1% of the total renewable energy generated worldwide. The lion’s share of renewable energy still lies in hydroelectric power, which is dependent on the vagaries of the weather and a good monsoon.
Whenever fossil fuels are burnt (for power generation, running vehicles etc) nitrogen oxides are released into the atmosphere causing severe pollution. With nitrogen polluting the air we breathe and also affecting the water and land, the natural balance of nitrogen present in the air (it is essential for plant and animal life) is affected. Moreover, burning of fossil fuels is known to cause smog and acid rain, which again is bad for the environment. Apart from nitrogen, fossil fuels are known to emit Ammonia into the air. Coal fired power plants spew nitrogen oxide emissions, adding to the woes of the planet. Improving energy efficiency is one of the ways to control greenhouse gas emissions in the atmosphere. Green Buildings focus on efficient energy management, thus contributing to a cleaner atmosphere, allowing us to breathe a sigh of relief. The primary contributor to the global warming is burning fossil fuels.
Hence, it is not very difficult to understand that energy efficiency is one of the most important factors in a Green Building. When we use more renewable energy and achieve high energy efficiency, we can move towards carbon neutrality and thereby prevent global warming.
Green buildings focus on fulfilling their energy needs by generating energy from non-fossil based resources like solar power or wind power. While some buildings can generate enough solar or wind power onsite itself to fulfill most of their energy requirements, some buildings have their green power generating systems located off-site.
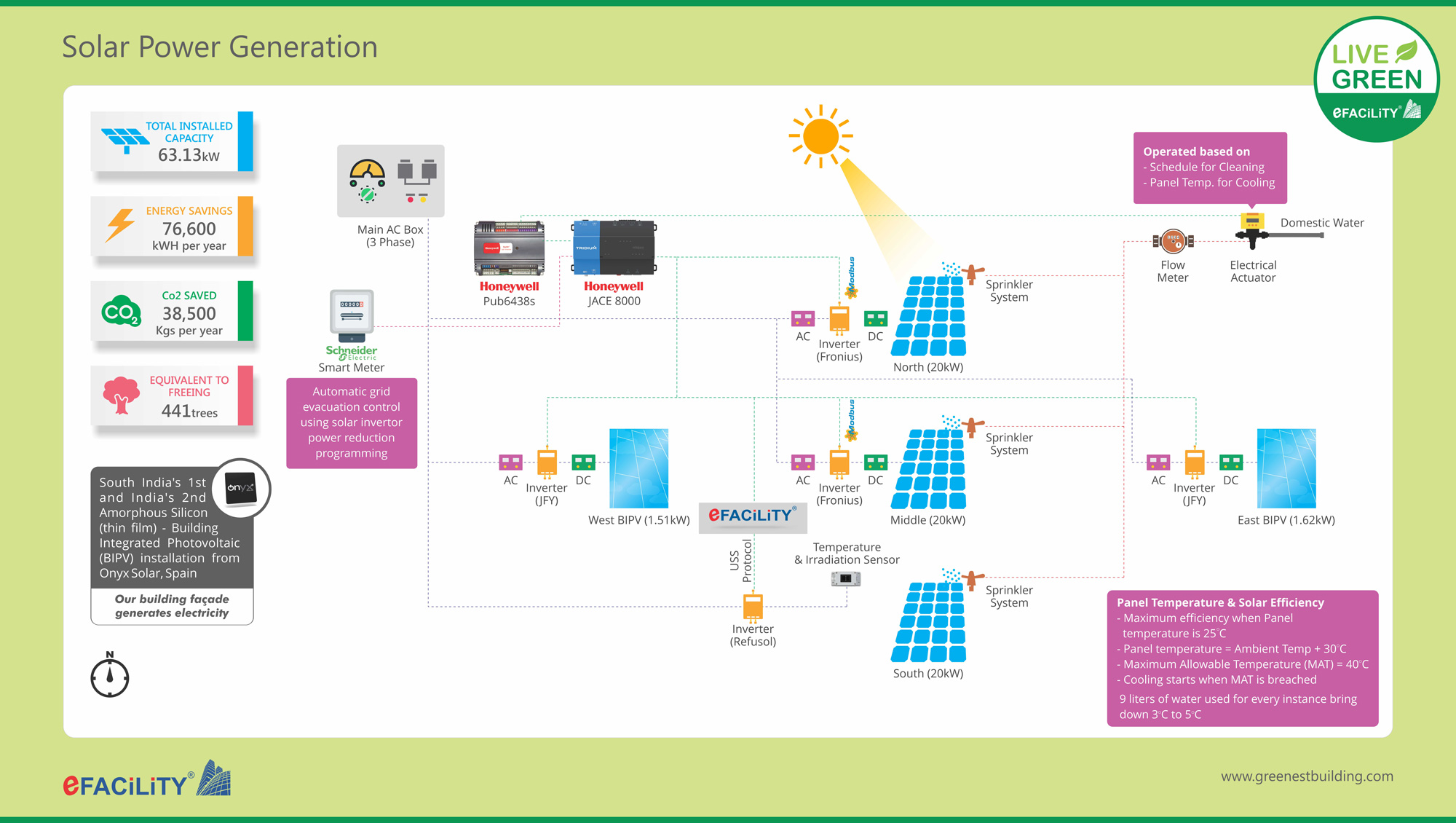
At eFACiLiTY® we are proud to say that our energy cost savings is a whopping 64%, thanks to the solar power we generate at our Green Building, maximization of day-light use, use of highly energy efficient systems, 100% automation reducing wastage apart from the various other energy saving initiatives implemented.
Atmosphere
The atmosphere in which we spend a good part of our time everyday has to be clean and healthy in order to bring out the best in us, and also to keep us healthy and free of diseases. It is not enough to install efficient filters and have an efficient air conditioning system that circulates fresh air inside a green building.
The refrigerants used in our air-conditioning systems, refrigerators and coolers etc. deplete the ozone layer and also cause global warming. By selecting the greenest available refrigerants in the these systems we implement, we can reduce the effects of global warming and ozone depletion.